
The importance of foundations in the building and its injuries
It may seem like a simple part of the overall build process, but proper execution of the foundations and the seat in any construction element is incredibly important, the main reason, any mistakes that can be made will simply get worse as we raise the building.
The main mission of the foundation of a building or in a simple house is that of distribute the loads it receives from the stresses of the structure and transmit them to the ground by means of surfaces calculated and adapted to the type of soil on which it rests. So we have good reason why its execution deserves more focus and attention to detail.
But… What are its main objectives and what should we take into account? Although it may seem like a simple question, this question actually covers quite a few books on spatial foundations, but even so, we asked some colleagues who are professionals in building foundations Piresa trying to obtain a clearer, more summarized and concise answer from the base on which a building rests.
Why is the foundation important?
Leaving aside its obviousness and structural support function that we can all recognize, the reality is that a good seat is the first step to building a solid and safe infrastructure, but there is more.
According to a statistical analysis on the pathologies in the building by means of the MUSAAT, the pathologies produced by the foundation they amount to almost 11%. So its importance in the execution of them, must be prioritized.

From the above table we can deduce that the areas where the greatest number of pathologies occur are the enclosures and distributions in the first place, followed by the roofs, installations, foundations and finishes. In total, these five items account for 73% of the pathologies claimed in the files under study.
the pathologies produced by the foundations amount to almost 11%
So ensuring that seats will not be produced or that, if produced, they will be compatible with the deformability of the building structure is an objective that we must treat and achieve with great care.
Remember that we have an article on how to review damage to homes after an earthquake that includes excellent manuals.
What points are important in determining the type of seat to be built?
Although we can see that it is a very broad field from a constructive perspective, in reality, so that a foundation has the mission of transmitting the weight of the building to the ground - from a technical perspective - you must comply with a series of preconditions and characteristics to treat it as such, which are:
- That it has, by itself, an adequate resistance to the loads that will be transmitted to it from the building structure and that in turn will distribute the land.
- What transmits the possible loads so that any deformations that may occur, both in the foundation itself and in the ground, are tolerated at the same time by the rest of the building.
- That the resulting constructive element remains stable over time, in the sense that it is not affected by the aggressiveness of the soil itself, nor by future modifications that may occur in its environment.
Understanding how to choose the type of foundation for a building, of a house or even of an industrial warehouse, it is usually relatively complex, except in some trivial cases. To have a broad perspective, we want to provide a scheme that simplifies the process of factor analysis to choose a foundation typology:

Based on the previous characteristics that we have listed above, we can consider that the key points in adopting a foundation are:
- The terrain resistance where we will proceed to cement It should be the most important factor that will determine the foundation solution to be adopted..
- The stresses that the ground supports are considerably lower than those of the materials that make up the structure.
- The foundations must have a surface greater than the columns or walls that transmit the load of the structural system.
- In addition to adequately transmit loads from the building to the groundIt must be able to prevent the occurrence of settlements that can damage the constructive element that it supports.
the resistance of the ground will be the most important factor that will determine the solution adopted

To decide the type of foundation to be built (If we talk about the land) It is necessary to take into account - especially - the following conditions:
- Know in detail the characteristics of the terrain (geotechnical study), especially the strata on which the foundation is expected to be supported.
- Take into account the water table.
- Place the foundation base in a place inaccessible to frost.
To decide the type of seat to be built (If we talk about the structure of the building), it is necessary to take into account - especially - the following conditions:
- Take many special precautions when laying on unconsolidated ground.
- Know all the characteristics of the loads transmitted by the building.
- Take into account the influence of nearby buildings on the ground.

What types of foundations are there?
Actually when establishing the classification before the different types of foundations, We could do them from approaches wants an extensive classification; for example, because of the way they work, the type of material, the way they transmit efforts … etc.
We, to define the types of lift in front of a building we went to Basic Document SE-C Foundations (Technical building Code) where they are divided into two large groups:Shallow foundations - direct and deep foundations:
1.- Shallow or direct foundations
The direct foundation It is the one that distributes the loads of the structure in a horizontal support plane. They are built shallow below the surface of the ground (Less than 4 meters), also called shallow foundation and they are:
-
Types of shallow foundations:
- Insulated shoes
- Combination shoes
- Running shoes
- Foundation pits
- Foundation slats
- Foundation slabs

So that we have a 3D vision and can see the complexity in its execution with the assembly of an isolated footing. We leave the following example of foundation isolated:

2.- Deep foundations
The objective is transmit the loads to deep layers that have a greater bearing capacity and resistance. Those that have a length greater than six meters, or that the relationship between the height and the width of the foundation exceeds the value of five are considered.
-
Types of deep foundations
- Isolated piles
- Pile group
- Piloted zones
- Micropiles

We remember thattypes of piles reach an important variety and are classified in many ways (without accounting for new techniques, designs, machinery and technologies) we could distinguish them mainly by:
- The way of working
- By the type of pile material (Wood, reinforced concrete … etc)
- By its cross section
- For its constructive procedure
- Driven precast piles
- Piles concreted «in situ»

Also, micropiling or injections of expansive resins are used in the event of a faulty contact between our building and the ground with the aim of reinforce the structure To stabilize the building, underpinning of foundations is common and avoids the execution of costly works.
Now, since we have a general vision, we have to go into depth - although we obviously skip the technical part of calculations, which is what specialized companies are for - we would like to provide a series of technical guides that are very useful for the architectural professional. and engineering …
Check the relevant points in the execution of the work
These three foundation manuals they form a verification «check list», to determine the relevant points for the direction of execution of work on foundations and verify its justification:
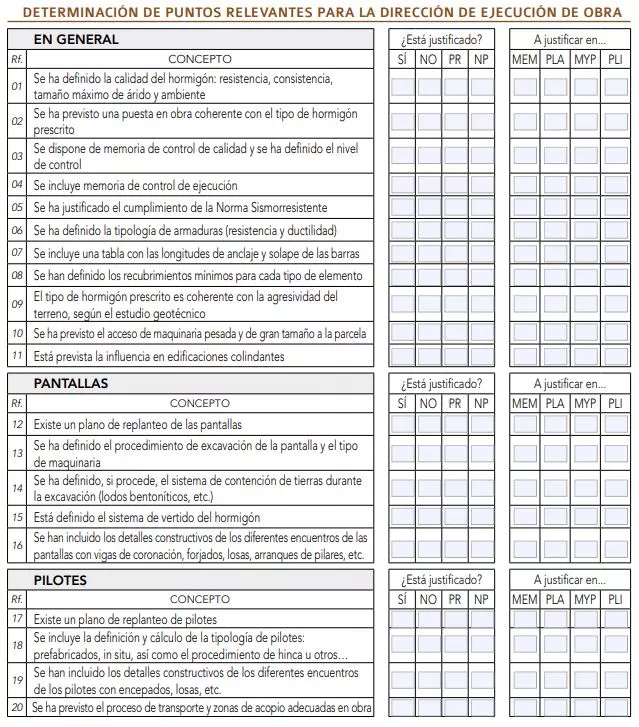
The three supporting documents are:
- Shallow foundations and walls
- Deep foundations
- Concrete floors
Common problems, foundation injuries and deficiencies
To know what are the common problems in a foundation, what are your injuries or deficiencies, the optimal design and trying to adopt some constructive technical recommendations to solve any problem, can be a challenge for every professional.
But we have 6 exceptional technical guidance documents - totally free - that give us very interesting data according to the type of foundation used we will get the foundation pathologies. These documents in file format are internally structured as:
Pathologies in foundations
- Constructive unit and description
- Possible areas of the structure - building affected
- Common problems,
- Injuries and deficiencies,
- Constructive technical recommendations
For example, part of the file on footing surface foundation pathology would be:

The six documents - tabs that deal with common problems are:
- Deep foundations: concrete walls
- Shallow foundations: footings
- Shallow foundations: foundation slabs
- Concrete floors
- Continuous or pile screen: Waterproofing and drainage
- Deep foundations: piles
Although we have undoubtedly left many aspects of interest, at least we are convinced that after reading, today we have learned a little more.
If you liked this article, share it!


