
Guide to glazing in enclosures
On the buildings, from an energy point of view, the windows with their glazing pertinent and the carpentry in general that will close the gaps of the envelope, are the weak point of all construction. They are the main thermal bridge on which we must study and act to benefit from better insulation on the building's skin.
To this day, we still continue to design buildings where the economic part of exterior cladding with glass Good quality insulation is quite scarce in relation to other issues in the building that are possibly more aesthetic and visual to the potential buyer.
We think more about the future commercialization of the building than about adding an added value to that home, office or commercial premises by reducing consumption or improving habitability with glazed joinery duly that provide added value on effective acoustics, bringing more light to the home or providing palpable energy savings in air conditioning and heating.
Between 25% and 30% of our heating or air conditioning needs are due to losses due to bad exterior enclosures in homes

These are benefits that must be explained to future owners so that they understand that the constructive quality that resides in a house, for example, is not always having the best marble floor or the latest kitchen in design.
 According to the company specializing in enclosures of glass curtains high-end Acristalia, between 25% and 30% of our heating or air conditioning needs are due to heat losses that originate in the windows.
According to the company specializing in enclosures of glass curtains high-end Acristalia, between 25% and 30% of our heating or air conditioning needs are due to heat losses that originate in the windows.
We want to find out why we should adopt a efficient and insulating enclosure quantifying its energy and economic advantages since if we see the attached image, the single glazing It is a leader in Europe, that is to say, of low quality.
As a representative element and key link in the building envelope, we will adopt the windows in the exterior enclosure as a basis for study …
How do windows respond to hot or cold?
Although it is a question with an obvious answer for many professionals in the architecture and construction sector, we would like to look at it from the graphical perspective based on its thermal bridges according to relevant thermographic photographs of a home.
First from the cold input and heat output, going through the blind boxes and ending in the profiles section to have a global vision of their behavior:

Two elements are characterized as key points in all carpentry:
- Frame - profile (Including shutter - capialzado, if applicable), which on average represents between 35 and 25% of the opening surface and that among its main properties we find absorptivity and thermal transmittance from the point of view of insulation.
- Glasses (The glazing represents approximately 70% of the window surface), which has multiple characteristics that influence its behavior (thermal transmittance, solar factor, light transmission, the appearance itself… etc).
Types of glazed windows
We must remember that there is a wide range ofglazed window models, products and solutions for houses or any constructive element such as: sliding windows or doors, folding enclosures, sliding enclosures or more specific covers with advanced technological features with mobile roofs that are practiced in some more modern enclosures and glass curtains without profiles.
Broadly speaking, we can classify the following solutions of types of glazed enclosure:
- Exterior enclosure with sliding sliding glass (With sliding leaves).
- Exterior enclosure with folding glass (folding sheets).
- Exterior enclosure with half-height glass.
- Exterior enclosure with glass curtains.
- Exterior enclosure with glass on mobile and fixed roofs.
- Double glazing enclosure.
Glass curtains
They represent a novel solution, within the glass joinery, with the particularity that they are bonded glass sheets each other on the side, where most pieces only have a frame on their upper and lower face. To see it better, in the following image that corresponds to an example of glass curtains on terrace, a glazed porch:

They are structures normally with PVC joinery commonly used in terrace glazing, in gardens or balconies of homes without profiles, which take advantage of their capabilities to obtain advantages over the capture of natural lighting in large spaces while protecting against meteorological actions and of course, with an insulating effect as we will see later.
The glass curtain provides greater luminosity than other closing techniques
Opinions of these types of structures, many, the drawbacks of glass curtains They are mainly its cleanliness when crystallizing a considerable surface and the cost, nowadays, in terms of resistance as a rule there are no problems. From the technical and plans perspective we would find the following profiles:

An example of how thermal insulation and sun protection works when glaze a terrace it would be the following scheme:

What are the factors in the thermal insulation of a window
The frame and the glass, working together, are responsible in the medium and long term for providing us with adequate benefits of well-being and comfort in our home, without counting the economic savings that we can obtain by outlining better insulation. The combination of both is what gives us the ability to window insulation:

About him thermal insulation in carpentry, the main factors that influence the energy saving of a window are:
- Profile material: For example, in PVC carpentry the thermal bridges are minimal or nonexistent.
- The level of tightness: A window that has an adequate level of airtightness will guarantee good thermal insulation.
- The quality of the crystal: The right glazing comes into play here, which will favor important benefits, solar captures or long-term energy savings, among other issues that we will analyze later.
Installing high-performance glass is a very important factor in saving energy
Remembering the concept of transmittancethermal «U» (U = W / m2K) for its importance. The term represents the amount of heat that passes through a material, which together is the thermal insulation capacity that, for example, a door or window can have, that is, the lower the «U», the greater the insulation capacity. will have the window or door. To understand the calculations of how it is obtained:

As we have seen, insulating glazing They are very important and we are going to see which is the best option for our home …
Classification scheme of glasses according to their composition
Since it is complex to go into the composition and groups, we wanted to provide a scheme that perfectly summarizes the possible variants and other aspects such as thickness, color, type of moon, reflective layer … etc. (Clicking on the image enlarges)

What types of window glass are there?
Depending on the layers, the deposited material or the deposition system, the characteristics and performance of the glass obtained can be very different. At a commercial level and from the user's perspective, it is much more useful to classify them according to the benefits and utility that they provide us:
- The simple or also called monolithics: Usually they are those that are installed in windows of a lower quality or traditional sliding doors. From the perspective of insulation they have few properties.
- With camera: They are those formed by two pieces of glass between which there is an air chamber that increases thermal insulation.
- Safety or laminated ones: It is the union of several glass plates that reinforces its resistance.
- Those designated with acoustic treatment: They are laminated glasses to which we add the use of an acoustic PVB.
- Low Emissivity Glasses: Reduce heat losses from inside the building through the glazing. Its placement can be on the inner or outer sheet of the double glazing, without varying its insulation performance (U W / m2 K value). They are particularly effective in unexposed orientations since, apart from saving energy, they avoid the "cold wall effect" or sensation of "heat theft" that the human body experiences in the presence of the cold surface of a normal glazing with low outside temperature .

- Solar Control Glasses: They reduce the inputs of heat produced by sunlight, reducing the greenhouse effect. They should be placed in carpentry that can receive direct solar radiation (A perfect example of use is glass curtains in enclosures for terraces). The loss of heat gains in cold seasons must be calibrated or supplemented with low-emissivity glass to reinforce the insulation in winter. Among the solar control glasses, the highly selectivity glasses stand out.
It must be considered that we can also combine them to strengthen certain characteristics.
Factors in the thermal losses of the glass
- Thermal transmittance U (W / m2K): Although we have already talked about this term before, we remember that it represents the difference in temperatures between both sides of the glass.
- The solar factor (g): It is the term that defines the solar protection offered by a glazing. The% of heat that enters a window when the sun falls on it. (the less the factor, the greater the protection)

- Light transmission (TL): It refers to the amount of light that a glazing lets through with reference to the light existing on the outside.
- The appearance: They are the shades of the glass or the color.
How to choose window glazing?
The greater participation in surface area on the window, means that the gains produced in the U of the glazing have a greater impact than those achieved by the same gain on the U of the frame. (See also the article on efficient windows and their joinery)
Better to have and buy good insulating glass than to spend more money on frames
As advice, from the perspective of the units of insulating glass (North orientations), low values of U (W / m2K) should be taken into account.
The glazing must allow the lowest thermal transmittance and the maximum light transmission. To increase thermal insulation we must use low-emissivity glass where we have the types of glazing:
- Single glazing
- Double glazing
- High performance double glazing
- High performance triple glazing

In windows that receive direct solar radiation (Houses with South, Southeast, Southwest, East and West orientations) the glasses with a low solar factor strongly reduce the heat contributed by the sun.
In hot climates or with summer conditions, it is advisable to install glazing with a reinforced solar factor (Always ensuring that the U values are low)
How much do we save by changing the windows at home?
How what we are normally going to practice is changing windows or glaze a terrace with the intention of improving and saving economically on our electricity bill.
First, we will see what kinds ofnew windows in facade with energy efficiency class in carpentry and PVC profiles (We leave aside those of aluminum and wood) we will find ourselves in the market commonly, regardless of our budget or prices, we can see in general:
Via Guide of Work and Reform - Laplataforma.es
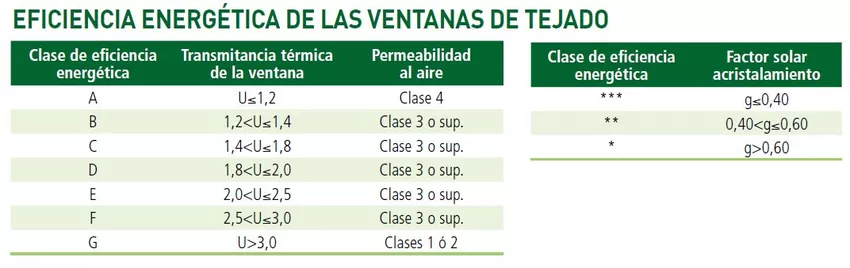
If we move to windows on rooftops, We find the following indicative table:
Via Guide of Work and Reform - Laplataforma.es
We wanted to provide a scheme that clarifies the where the savings come from changing the windows. The following image comes from Tecnalia about the report "Determination of the importance of the factors of influence of a window in the energy demand of a building".

On every 100 Euros saved, the report breaks down where they come from and from which parts of the window:
After seeing the energy savings that we can achieve thanks to the change of the exterior carpentry and studying its behavior, we hope to have solved some doubts that can help us to design more efficient buildings.
To find out more from a professional perspective:
- Glazed enclosure technical guide from HERE (IDAE)
- Rehabilitation and glazed enclosures from HERE (Andimat)
- Guide to efficient windows from HERE (Fenercom)
If you liked the article, rate and share!


